How Accurate is your GPS ?
| Information - TRAKGPS Articles | ||||||||||||||||||||
How close are you really to where your GPS says you are?
Computer Voice Generated version - PLAY Measure the accuracy First you have to know where you really are. Obviously, if you know where you really are, you can check the GPS. But if you knew where you were you wouldn't need the GPS. So how do you know what your position error is when you don't know exactly where you are? It's not obvious, but the short answer is that you don't. Just like if you buy a lottery ticket; you can't tell if you've won or not until they announce the correct numbers. You can't know the correct number in advance, but you can estimate your chances of winning anyway. Estimate the accuracy As you sit, wondering where you are, watching your GPS, you notice that the position it gives wanders around. Some of those numbers must be accurate, but which ones are they? If you wait long enough, you can take the average and find your position with improved accuracy. Then you can take all of the positions and find out how far they are from that average position. From that you could calculate what the average deviation was. The next time you used the GPS, you could figure that the GPS position would vary in about the same way, so you could use your "average deviation" numbers to estimate the accuracy of your new GPS position. The only problem is that these numbers do vary, so it's not this simple. But the idea is good. Sources of error There are several sources of error in any GPS reading. Some of these errors are due to natural causes, and some error is introduced on purpose (SA). You can read more about the "error budget" and Selective Availability elsewhere. These numbers vary, but not so much as the position errors. There's a famous computing principle called GIGO -- garbage in, garbage out. Here it's not really garbage in; they're just "little" errors. When the GPS uses these inputs to solve for your position, it is only natural that your position is going to be in error too. If you study the equations that the GPS uses to solve for the position, you can analyze what the effects of these input errors will be and you can find a formula which predicts what the output errors will be. This formula predicts what the error in the GPS position will be and presents a number to the user. It's like a magnifying effect, since it normally makes the final error bigger than the input errors. The magnifying factor is called DOP -- Dilution of Precision. Dilution of Precision The DOP factor is used in a very simple equation: SD(position) = DOP * SD(inputs) This means that the standard deviation of the position is simply the standard deviation of the inputs multiplied times the DOP factor. Of course, this formula isn't as simple as it looks, since for GPS a multidimensional solution is required, and therefore matrix mathematics is used. But the idea is good. One interesting thing about DOP is that it does not depend on the anything that cannot be predicted in advance. It only depends on the positions of the GPS satellites relative to the GPS receiver's location. The satellite positions can be calculated in advance, so you can determine the quality of your GPS position fix in advance, without even using the GPS system. Satellite geometry DOP only depends on the position of the satellites: how many satellites you can see, how high they are in the sky, and the bearing towards them. This is often refered to as the geometry. The satellites move, so the geometry varies with time, but it is very predictable. VDOP, HDOP, etc DOP is often divided up into components. These componets are used because the accuracy of the GPS system varies. For example horizontal position can usually be measured more accurately than vertical position. The input errors are the same, but the geometry may favor one direction over another. VDOP is vertical DOP; HDOP is horizontal DOP. There are also PDOP for 3D positions, TDOP for time, and GDOP for geometic DOP (which is everything all together). For example, a DOP of 2 means that whatever the input errors were, the final error will twice as big. We can use the DOP value to estimate the possible error of your position. If you know (or guess) that the UERE is 25 meters ... (where UERE is user estimated range error: the standard deviation of the errors in the psuedoranges of the satellites at the user's position) ... then you know that your position error has a standard deviation of 50 meters. If we don't know the input errors, we can just use the DOP value as an indicator of how good the conditions are for making GPS position measurements. ie, one with a DOP of 2 is better than one with a DOP of 4. Some ways to improve accuracy Use DGPS to reduce the errors in the inputs. Improve DOP by using more satellites. Take your measurements when the satellites are spread out over the sky. Average the GPS position readings over time. Reaching for a metaphor To understand how DOP is calculated requires understanding statistics. If you just want to use it, and if you don't know statistics, just think about betting. Pick a sport, any sport. Whether it is pool, bowling, basketball, diving, the stock market, or whatever. There are difficult shots and easy shots. Difficult things are riskier. DOP is a rating of the difficulty of getting a good position out of a particular combination of GPS satellites. With a high DOP, don't expect an accurate position; it could still be good, but probably it's not. With low DOP, the position is probably closer to being right, but remember it's an estimate, not a guarantee. What's the signal? GPS satellites transmit two low power radio signals, designated L1 and L2. Civilian GPS uses the L1 frequency of 1575.42 MHz in the UHF band. The signals travel by line of sight, meaning they will pass through clouds, glass and plastic but will not go through most solid objects such as buildings and mountains. A GPS signal contains three different bits of information — a pseudorandom code, ephemeris data and almanac data. The pseudorandom code is simply an I.D. code that identifies which satellite is transmitting information. Ephemeris data tells the GPS receiver where each GPS satellite should be at any time throughout the day. Each satellite transmits ephemeris data showing the orbital information for that satellite and for every other satellite in the system. Almanac data, which is constantly transmitted by each satellite, contains important information about the status of the satellite (healthy or unhealthy), current date and time. This part of the signal is essential for determining a position. Sources of GPS signal errors Factors that can degrade the GPS signal and thus affect accuracy include the following: * Ionosphere and troposphere delays — The satellite signal slows as it passes through the atmosphere. The GPS system uses a built-in model that calculates an average amount of delay to partially correct for this type of error. * Signal multipath — This occurs when the GPS signal is reflected off objects such as tall buildings or large rock surfaces before it reaches the receiver. This increases the travel time of the signal, thereby causing errors. * Receiver clock errors — A receiver's built-in clock is not as accurate as the atomic clocks onboard the GPS satellites. Therefore, it may have very slight timing errors. * Orbital errors — Also known as ephemeris errors, these are inaccuracies of the satellite's reported location. * Number of satellites visible — The more satellites a GPS receiver can "see," the better the accuracy. Buildings, terrain, electronic interference, or sometimes even dense foliage can block signal reception, causing position errors or possibly no position reading at all. GPS units typically will not work indoors, underwater or underground. * Satellite geometry/shading — This refers to the relative position of the satellites at any given time. Ideal satellite geometry exists when the satellites are located at wide angles relative to each other. Poor geometry results when the satellites are located in a line or in a tight grouping. * Intentional degradation of the satellite signal — Selective Availability (SA) is an intentional degradation of the signal once imposed by the U.S. Department of Defense. SA was intended to prevent military adversaries from using the highly accurate GPS signals. The government turned off SA in May 2000, which significantly improved the accuracy of civilian GPS receivers. Error analysis for the Global Positioning System
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The analysis of errors computed using the Global Positioning System
is important for understanding how GPS works, and for knowing what
magnitude errors should be expected. The Global Positioning System makes
corrections for receiver clock errors and other effects but there are
still residual errors which are not corrected. The Global Positioning
System (GPS) was created by the United States Department of Defense
(DOD) in the 1970s. It has come to be widely used for navigation both by
the U.S. military and the general public.User vehicle position is computed by the receiver based on data received from the satellites. Errors depend on geometric dilution of precision and the sources listed in the table below. Contents
Overview
 , of about 1 meter. The standard deviations, , of about 1 meter. The standard deviations,  ,
for the coarse/acquisition (C/A) and precise codes are also shown in
the table. These standard deviations are computed by taking the square
root of the sum of the squares of the individual components (i.e., RSS
for root sum squares). To get the standard deviation of receiver
position estimate, these range errors must be multiplied by the
appropriate dilution of precision terms and then RSS'ed with the
numerical error. Electronics errors are one of several
accuracy-degrading effects outlined in the table above. When taken
together, autonomous civilian GPS horizontal position fixes are
typically accurate to about 15 meters (50 ft). These effects also reduce
the more precise P(Y) code's accuracy. However, the advancement of
technology means that today, civilian GPS fixes under a clear view of
the sky are on average accurate to about 5 meters (16 ft) horizontally. ,
for the coarse/acquisition (C/A) and precise codes are also shown in
the table. These standard deviations are computed by taking the square
root of the sum of the squares of the individual components (i.e., RSS
for root sum squares). To get the standard deviation of receiver
position estimate, these range errors must be multiplied by the
appropriate dilution of precision terms and then RSS'ed with the
numerical error. Electronics errors are one of several
accuracy-degrading effects outlined in the table above. When taken
together, autonomous civilian GPS horizontal position fixes are
typically accurate to about 15 meters (50 ft). These effects also reduce
the more precise P(Y) code's accuracy. However, the advancement of
technology means that today, civilian GPS fixes under a clear view of
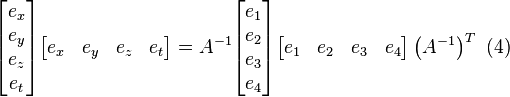
the sky are on average accurate to about 5 meters (16 ft) horizontally.The term user equivalent range error (UERE) refers to the error of a component in the distance from receiver to a satellite. These UERE errors are given as ± errors thereby implying that they are unbiased or zero mean errors. These UERE errors are therefore used in computing standard deviations. The standard deviation of the error in receiver position,  , is computed by multiplying PDOP (Position Dilution Of Precision) by , is computed by multiplying PDOP (Position Dilution Of Precision) by  , the standard deviation of the user equivalent range errors. , the standard deviation of the user equivalent range errors.  is computed by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the individual component standard deviations. is computed by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the individual component standard deviations.PDOP is computed as a function of receiver and satellite positions. A detailed description of how to calculate PDOP is given in the section, geometric dilution of precision computation (GDOP).  for the C/A code is given by: for the C/A code is given by: , again for the C/A code is given by: , again for the C/A code is given by:Signal arrival time measurementThe position calculated by a GPS receiver requires the current time, the position of the satellite and the measured delay of the received signal. The position accuracy is primarily dependent on the satellite position and signal delay.To measure the delay, the receiver compares the bit sequence received from the satellite with an internally generated version. By comparing the rising and trailing edges of the bit transitions, modern electronics can measure signal offset to within about one percent of a bit pulse width, 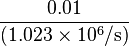 , or approximately 10 nanoseconds for the C/A code. Since GPS signals propagate at the speed of light, this represents an error of about 3 meters. , or approximately 10 nanoseconds for the C/A code. Since GPS signals propagate at the speed of light, this represents an error of about 3 meters.This component of position accuracy can be improved by a factor of 10 using the higher-chiprate P(Y) signal. Assuming the same one percent of bit pulse width accuracy, the high-frequency P(Y) signal results in an accuracy of  or about 30 centimeters. or about 30 centimeters.Atmospheric effectsInconsistencies of atmospheric conditions affect the speed of the GPS signals as they pass through the Earth's atmosphere, especially the ionosphere. Correcting these errors is a significant challenge to improving GPS position accuracy. These effects are smallest when the satellite is directly overhead and become greater for satellites nearer the horizon since the path through the atmosphere is longer (see airmass). Once the receiver's approximate location is known, a mathematical model can be used to estimate and compensate for these errors.Ionospheric delay of a microwave signal depends on its frequency. It arises from ionized atmosphere (see Total electron content). This phenomenon is known as dispersion and can be calculated from measurements of delays for two or more frequency bands, allowing delays at other frequencies to be estimated.[1] Some military and expensive survey-grade civilian receivers calculate atmospheric dispersion from the different delays in the L1 and L2 frequencies, and apply a more precise correction. This can be done in civilian receivers without decrypting the P(Y) signal carried on L2, by tracking the carrier wave instead of the modulated code. To facilitate this on lower cost receivers, a new civilian code signal on L2, called L2C, was added to the Block IIR-M satellites, which was first launched in 2005. It allows a direct comparison of the L1 and L2 signals using the coded signal instead of the carrier wave. The effects of the ionosphere generally change slowly, and can be averaged over time. Those for any particular geographical area can be easily calculated by comparing the GPS-measured position to a known surveyed location. This correction is also valid for other receivers in the same general location. Several systems send this information over radio or other links to allow L1-only receivers to make ionospheric corrections. The ionospheric data are transmitted via satellite in Satellite Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) such as Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) (available in North America and Hawaii), EGNOS (Europe and Asia) or Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS) (Japan), which transmits it on the GPS frequency using a special pseudo-random noise sequence (PRN), so only one receiver and antenna are required. Humidity also causes a variable delay, resulting in errors similar to ionospheric delay, but occurring in the troposphere. This effect both is more localized and changes more quickly than ionospheric effects, and is not frequency dependent. These traits make precise measurement and compensation of humidity errors more difficult than ionospheric effects.[citation needed] Changes in receiver altitude also change the delay, due to the signal passing through less of the atmosphere at higher elevations. Since the GPS receiver computes its approximate altitude this error is relatively simple to correct, either by applying a function regression or correlating margin of atmospheric error to ambient pressure using a barometric altimeter.[citation needed] Multipath effectsGPS signals can also be affected by multipath issues, where the radio signals reflect off surrounding terrain; buildings, canyon walls, hard ground, etc. These delayed signals can cause inaccuracy. A variety of techniques, most notably narrow correlator spacing, have been developed to mitigate multipath errors. For long delay multipath, the receiver itself can recognize the wayward signal and discard it. To address shorter delay multipath from the signal reflecting off the ground, specialized antennas (e.g., a choke ring antenna) may be used to reduce the signal power as received by the antenna. Short delay reflections are harder to filter out because they interfere with the true signal, causing effects almost indistinguishable from routine fluctuations in atmospheric delay.Multipath effects are much less severe in moving vehicles. When the GPS antenna is moving, the false solutions using reflected signals quickly fail to converge and only the direct signals result in stable solutions. Ephemeris and clock errorsWhile the ephemeris data is transmitted every 30 seconds, the information itself may be up to two hours old. Variability in solar radiation pressure[2] has an indirect effect on GPS accuracy due to its effect on ephemeris errors. If a fast time to first fix (TTFF) is needed, it is possible to upload a valid ephemeris to a receiver, and in addition to setting the time, a position fix can be obtained in under ten seconds. It is feasible to put such ephemeris data on the web so it can be loaded into mobile GPS devices.[3] See also Assisted GPS.The satellite's atomic clocks experience noise and clock drift errors. The navigation message contains corrections for these errors and estimates of the accuracy of the atomic clock. However, they are based on observations and may not indicate the clock's current state. These problems tend to be very small, but may add up to a few meters (tens of feet) of inaccuracy.[4] For very precise positioning (e.g., in geodesy), these effects can be eliminated by differential GPS: the simultaneous use of two or more receivers at several survey points. In the 1990s when receivers were quite expensive, some methods of quasi-differential GPS were developed, using only one receiver but reoccupation of measuring points. At the TU Vienna the method was named qGPS and post processing software was developed.[citation needed] Geometric dilution of precision computation (GDOP)Computation of geometric dilution of precisionThe concept of geometric dilution of precision was introduced in the section, error sources and analysis. Computations were provided to show how PDOP was used and how it affected the receiver position error standard deviation.When visible GPS satellites are close together in the sky (i.e., small angular separation), the DOP values are high; when far apart, the DOP values are low. Conceptually, satellites that are close together cannot provide as much information as satellites that are widely separated. Low DOP values represent a better GPS positional accuracy due to the wider angular separation between the satellites used to calculate GPS receiver position. HDOP, VDOP, PDOP and TDOP are respectively Horizontal, Vertical, Position (3-D) and Time Dilution of Precision. Figure 3.1 Dilution of Precision of Navstar GPS data from the U.S. Coast Guard provide a graphical indication of how geometry affect accuracy. We now take on the task of how to compute the dilution of precision terms. As a first step in computing DOP, consider the unit vector from the receiver to satellite i with components 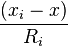 , ,  , and , and  where the distance from receiver to the satellite, where the distance from receiver to the satellite,  , is given by: , is given by: and and  denote the position of the receiver and denote the position of the receiver and 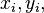 and and 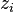 denote the position of satellite i. These x, y, and z
components may be components in a North, East, Down coordinate system a
South, East, Up coordinate system or other convenient system. Formulate
the matrix A as: denote the position of satellite i. These x, y, and z
components may be components in a North, East, Down coordinate system a
South, East, Up coordinate system or other convenient system. Formulate
the matrix A as: is used quite often where we have used d. However the elements of the Q
matrix do not represent variances and covariances as they are defined
in probability and statistics. Instead they are strictly geometric
terms. Therefore d as in dilution of precision is used. PDOP, TDOP and
GDOP are given by is used quite often where we have used d. However the elements of the Q
matrix do not represent variances and covariances as they are defined
in probability and statistics. Instead they are strictly geometric
terms. Therefore d as in dilution of precision is used. PDOP, TDOP and
GDOP are given by
The horizontal dilution of precision, 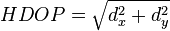 , and the vertical dilution of precision, , and the vertical dilution of precision,  , are both dependent on the coordinate system used. To correspond to the local horizon plane and the local vertical, x, y, and z should denote positions in either a North, East, Down coordinate system or a South, East, Up coordinate system. , are both dependent on the coordinate system used. To correspond to the local horizon plane and the local vertical, x, y, and z should denote positions in either a North, East, Down coordinate system or a South, East, Up coordinate system.Derivation of equations for computing geometric dilution of precisionThe equations for computing the geometric dilution of precision terms have been described in the previous section. This section describes the derivation of these equations. The method used here is similar to that used in "Global Positioning System (preview) by Parkinson and Spiker"Consider the position error vector,  ,
defined as the vector from the intersection of the four sphere surfaces
corresponding to the pseudoranges to the true position of the receiver. ,
defined as the vector from the intersection of the four sphere surfaces
corresponding to the pseudoranges to the true position of the receiver. where bold denotes a vector and where bold denotes a vector and  , ,  , and , and  denote unit vectors along the x, y, and z axes respectively. Let denote unit vectors along the x, y, and z axes respectively. Let  denote the time error, the true time minus the receiver indicated time. Assume that the mean value of the three components of denote the time error, the true time minus the receiver indicated time. Assume that the mean value of the three components of  and and  are zero. are zero. , ,  , ,  , and , and  are the errors in pseudoranges 1 through 4 respectively. This equation comes from linearizing the Newton-Raphson equation relating pseudoranges to receiver position, satellite positions, and receiver clock errors. Multiplying both sides by are the errors in pseudoranges 1 through 4 respectively. This equation comes from linearizing the Newton-Raphson equation relating pseudoranges to receiver position, satellite positions, and receiver clock errors. Multiplying both sides by  there results there results
 Note: 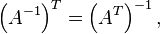 since since  Substituting for 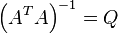 there follows there follows
Selective availabilityGPS included a (currently disabled) feature called Selective Availability (SA) that adds intentional, time varying errors of up to 100 meters (328 ft) to the publicly available navigation signals. This was intended to deny an enemy the use of civilian GPS receivers for precision weapon guidance.SA errors are actually pseudorandom, generated by a cryptographic algorithm from a classified seed key available only to authorized users (the U.S. military, its allies and a few other users, mostly government) with a special military GPS receiver. Mere possession of the receiver is insufficient; it still needs the tightly controlled daily key. Before it was turned off on May 2, 2000, typical SA errors were about 50 m (164 ft) horizontally and about 100 m (328 ft) vertically.[6] Because SA affects every GPS receiver in a given area almost equally, a fixed station with an accurately known position can measure the SA error values and transmit them to the local GPS receivers so they may correct their position fixes. This is called Differential GPS or DGPS. DGPS also corrects for several other important sources of GPS errors, particularly ionospheric delay, so it continues to be widely used even though SA has been turned off. The ineffectiveness of SA in the face of widely available DGPS was a common argument for turning off SA, and this was finally done by order of President Clinton in 2000. DGPS services are widely available from both commercial and government sources. The latter include WAAS and the U.S. Coast Guard's network of LF marine navigation beacons. The accuracy of the corrections depends on the distance between the user and the DGPS receiver. As the distance increases, the errors at the two sites will not correlate as well, resulting in less precise differential corrections. During the 1990–91 Gulf War, the shortage of military GPS units caused many troops and their families to buy readily available civilian units. Selective Availability significantly impeded the U.S. military's own battlefield use of these GPS, so the military made the decision to turn it off for the duration of the war. In the 1990s, the FAA started pressuring the military to turn off SA permanently. This would save the FAA millions of dollars every year in maintenance of their own radio navigation systems. The amount of error added was "set to zero"[7] at midnight on May 1, 2000 following an announcement by U.S. President Bill Clinton, allowing users access to the error-free L1 signal. Per the directive, the induced error of SA was changed to add no error to the public signals (C/A code). Clinton's executive order required SA to be set to zero by 2006; it happened in 2000 once the U.S. military developed a new system that provides the ability to deny GPS (and other navigation services) to hostile forces in a specific area of crisis without affecting the rest of the world or its own military systems.[7] On 19 September 2007, the United States Department of Defense announced that future GPS III satellites will not be capable of implementing SA,[8] eventually making the policy permanent.[9] AntispoofingAnother restriction on GPS, antispoofing, remains on. This encrypts the P-code so that it cannot be mimicked by a transmitter sending false information. Few civilian receivers have ever used the P-code, and the accuracy attainable with the public C/A code is so much better than originally expected (especially with DGPS) that the antispoof policy has relatively little effect on most civilian users. Turning off antispoof would primarily benefit surveyors and some scientists who need extremely precise positions for experiments such as tracking tectonic plate motion.RelativitySpecial and general relativityAccording to the theory of relativity, due to their constant movement and height relative to the Earth-centered, non-rotating approximately inertial reference frame, the clocks on the satellites are affected by their speed. Special relativity predicts that the frequency of the atomic clocks moving at GPS orbital speeds will tick more slowly than stationary ground clocks by a factor of , or result in a delay of about 7 μs/day, where the orbital velocity is v = 4 km/s, and c = the speed of light. The time dilation effect has been measured and verified using the GPS. , or result in a delay of about 7 μs/day, where the orbital velocity is v = 4 km/s, and c = the speed of light. The time dilation effect has been measured and verified using the GPS.The effect of gravitational frequency shift on the GPS due to general relativity is that a clock closer to a massive object will be slower than a clock farther away. Applied to the GPS, the receivers are much closer to Earth than the satellites, causing the GPS clocks to be faster by a factor of 5×10^(−10), or about 45.9 μs/day. This gravitational frequency shift is noticeable. When combining the time dilation and gravitational frequency shift, the discrepancy is about 38 microseconds per day, a difference of 4.465 parts in 1010.[11] Without correction, errors in the initial pseudorange of roughly 10 km/day would accumulate. This initial pseudorange error is corrected in the process of solving the navigation equations. In addition the elliptical, rather than perfectly circular, satellite orbits cause the time dilation and gravitational frequency shift effects to vary with time. This eccentricity effect causes the clock rate difference between a GPS satellite and a receiver to increase or decrease depending on the altitude of the satellite. To compensate for the discrepancy, the frequency standard on board each satellite is given a rate offset prior to launch, making it run slightly slower than the desired frequency on Earth; specifically, at 10.22999999543 MHz instead of 10.23 MHz.[12] Since the atomic clocks on board the GPS satellites are precisely tuned, it makes the system a practical engineering application of the scientific theory of relativity in a real-world environment.[13] Placing atomic clocks on artificial satellites to test Einstein's general theory was proposed by Friedwardt Winterberg in 1955.[14] Calculation of time dilationTo calculate the amount of daily time dilation experienced by GPS satellites relative to Earth we need to separately determine the amounts due to special relativity (velocity) and general relativity (gravity) and add them together.The amount due to velocity will be determined using the Lorentz transformation. This will be:
In order to compensate for this gain, a GPS clock's frequency needs to be slowed by the fraction:
Sagnac distortionGPS observation processing must also compensate for the Sagnac effect. The GPS time scale is defined in an inertial system but observations are processed in an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed (co-rotating) system, a system in which simultaneity is not uniquely defined. A coordinate transformation is thus applied to convert from the inertial system to the ECEF system. The resulting signal run time correction has opposite algebraic signs for satellites in the Eastern and Western celestial hemispheres. Ignoring this effect will produce an east-west error on the order of hundreds of nanoseconds, or tens of meters in position.[16]Natural sources of interferenceSince GPS signals at terrestrial receivers tend to be relatively weak, natural radio signals or scattering of the GPS signals can desensitize the receiver, making acquiring and tracking the satellite signals difficult or impossible.Space weather degrades GPS operation in two ways, direct interference by solar radio burst noise in the same frequency band[17] or by scattering of the GPS radio signal in ionospheric irregularities referred to as scintillation.[18] Both forms of degradation follow the 11 year solar cycle and are a maximum at sunspot maximum although they can occur at anytime. Solar radio bursts are associated with solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs)[19] and their impact can affect reception over the half of the Earth facing the sun. Scintillation occurs most frequently at tropical latitudes where it is a night time phenomenon. It occurs less frequently at high latitudes or mid-latitudes where magnetic storms can lead to scintillation.[20] In addition to producing scintillation, magnetic storms can produce strong ionospheric gradients that degrade the accuracy of SBAS systems.[21] Artificial sources of interferenceIn automotive GPS receivers, metallic features in windshields,[22] such as defrosters, or car window tinting films[23] can act as a Faraday cage, degrading reception just inside the car.Man-made EMI (electromagnetic interference) can also disrupt or jam GPS signals. In one well-documented case it was impossible to receive GPS signals in the entire harbor of Moss Landing, California due to unintentional jamming caused by malfunctioning TV antenna preamplifiers.[24][25] Intentional jamming is also possible. Generally, stronger signals can interfere with GPS receivers when they are within radio range or line of sight. In 2002 a detailed description of how to build a short-range GPS L1 C/A jammer was published in the online magazine Phrack.[26] The U.S. government believes that such jammers were used occasionally during the War in Afghanistan, and the U.S. military claims to have destroyed six GPS jammers during the Iraq War, including one that was destroyed with a GPS-guided bomb.[27] A GPS jammer is relatively easy to detect and locate, making it an attractive target for anti-radiation missiles. The UK Ministry of Defence tested a jamming system in the UK's West Country on 7 and 8 June 2007.[28] Some countries allow the use of GPS repeaters to allow the reception of GPS signals indoors and in obscured locations; while in other countries these prohibited as the retransmitted signals can cause multi-path interference to other GPS receivers that receive data from both GPS satellites and the repeater. In the UK Ofcom now permits the use of GPS/GNSS Repeaters[29] under a 'light licensing' regime. Due to the potential for both natural and man-made noise, numerous techniques continue to be developed to deal with the interference. The first is to not rely on GPS as a sole source. According to John Ruley, "IFR pilots should have a fallback plan in case of a GPS malfunction".[30] Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) is a feature included in some receivers, designed to provide a warning to the user if jamming or another problem is detected. The U.S. military has also deployed since 2004 their Selective Availability / Anti-Spoofing Module (SAASM) in the Defense Advanced GPS Receiver (DAGR).[31] In demonstration videos the DAGR was shown to detect jamming and maintain its lock on the encrypted GPS signals during interference which caused civilian receivers to lose lock. The above has been collated from various sources for my own reading pleasure .. |


 C/A
C/A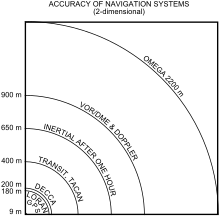






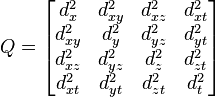
 ,
, , and
, and

 .
.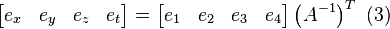 .
. .
.


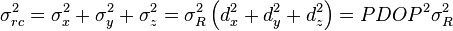 and
and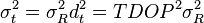

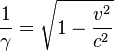

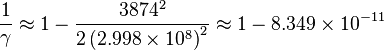

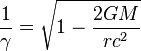
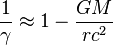
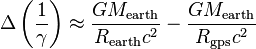

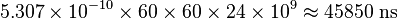
ReplyDeleteI have gone through the site and read all blogs and this is a nice one:
GPS Gamma surveys